All Kind Of Bone & Joints Pain
Orthopedic surgeries address a spectrum of bone and joint-related issues. Knee replacement surgery involves the replacement of a damaged knee joint with an artificial implant, offering relief to those with severe arthritis. Knee arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, diagnoses and treats knee problems with small incisions and quicker recovery. Hip replacement surgery substitutes a damaged hip joint with an artificial one, often resolving issues arising from arthritis or fractures. Shoulder arthroscopy examines and treats shoulder joint problems using minimally invasive techniques. Spinal fusion joins vertebrae to limit movement and alleviate spinal issues. Carpal tunnel release surgically relieves pressure on the wrist’s median nerve, while laminectomy addresses spinal cord or nerve compression. Joint injections and orthopedic fracture repairs offer localized relief for arthritis and severe fractures, respectively.
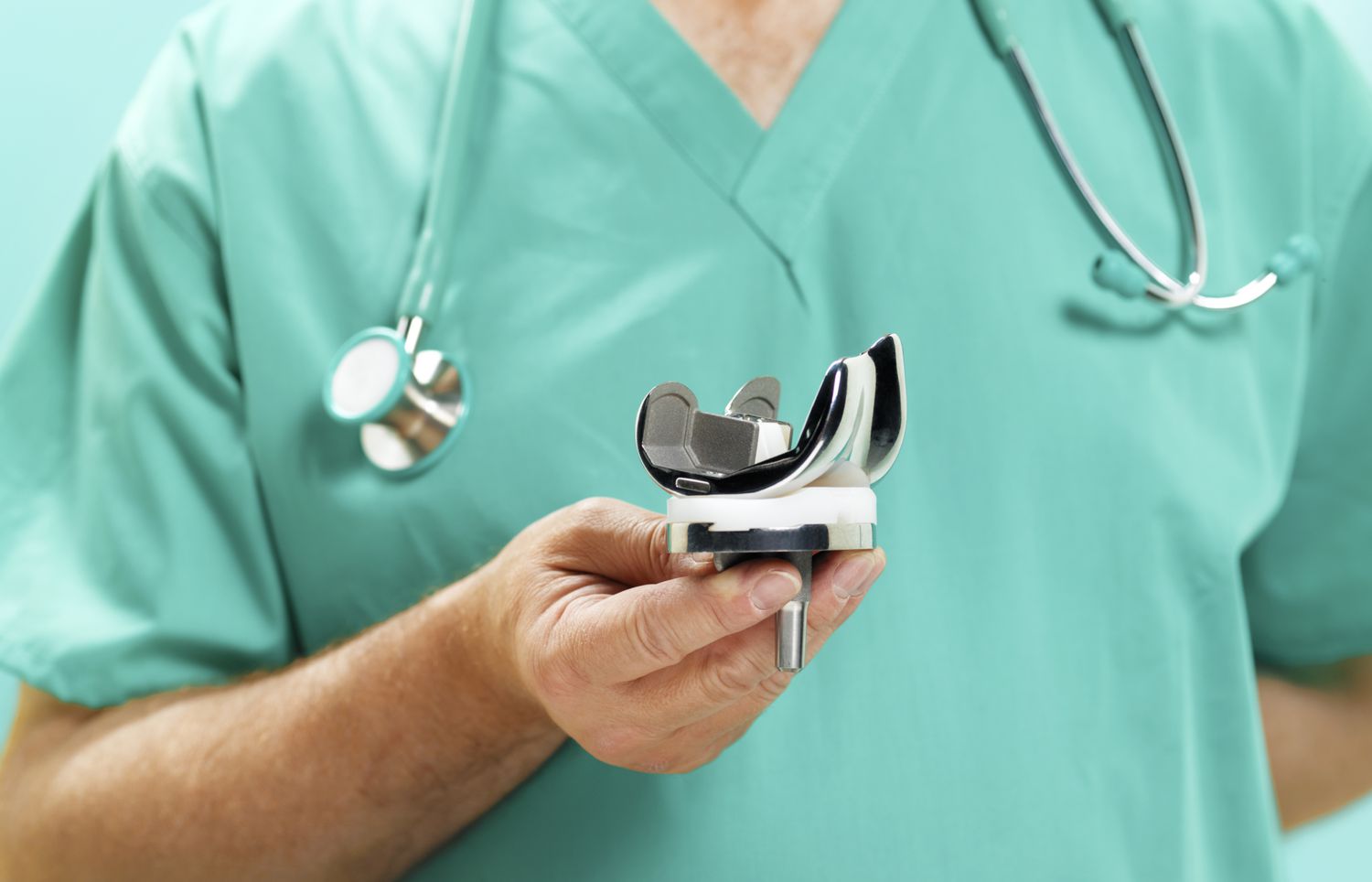
Knee Replacement:
Purpose: Knee replacement surgery addresses severe knee joint issues, commonly caused by arthritis or degeneration.
Procedure: Damaged portions of the knee joint are replaced with artificial implants, aiming to restore function and reduce pain.
Indications: Recommended when conservative treatments fail, and the knee condition significantly impairs daily life.
Mobility Improvement: The primary goal is to enhance mobility and alleviate discomfort, enabling individuals to regain an active lifestyle.
Recovery: Involves a post-surgical recovery period with rehabilitation and physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility.
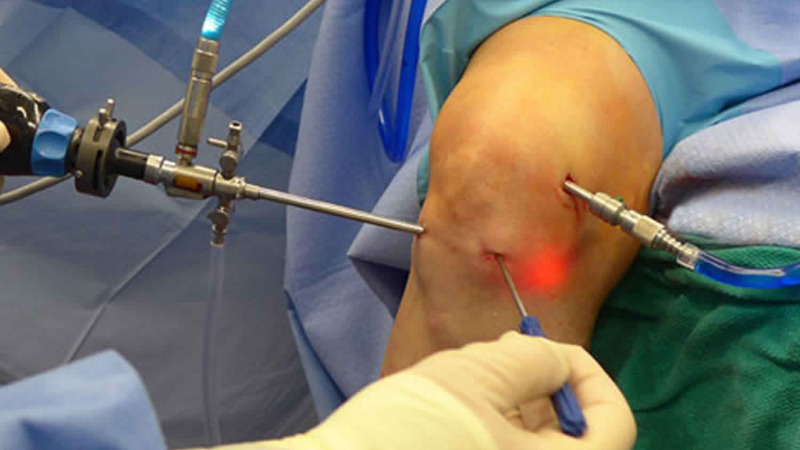
Knee Arthroscopy:
Purpose: Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to diagnose and treat various knee joint issues.
Procedure: Small incisions are made around the knee, and an arthroscope (a small camera) is inserted to visualize and address problems within the joint.
Indications: Commonly used for conditions like meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage damage, offering a quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic: Not only does it allow for the diagnosis of issues, but knee arthroscopy also enables the surgeon to perform therapeutic interventions during the same procedure.
Recovery: Typically involves a faster recovery time and less post-operative pain compared to traditional open surgery, making it a preferred option for certain knee conditions.
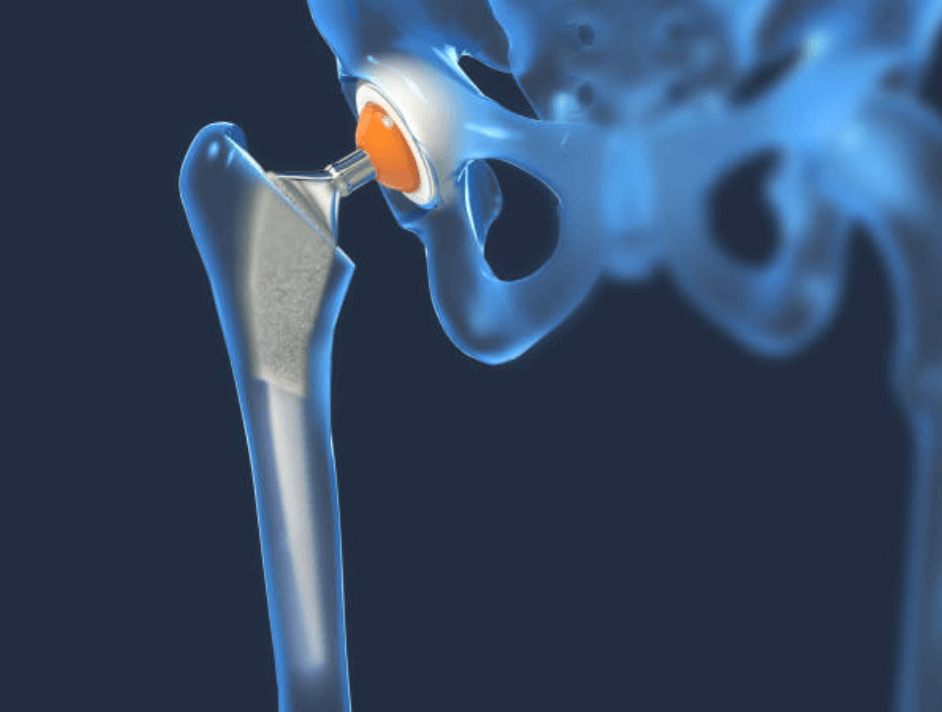
Hip Replacement:
Purpose: Hip replacement surgery is performed to address severe hip joint issues, often caused by conditions like arthritis or hip fractures.
Procedure: During the surgery, the damaged hip joint is replaced with an artificial implant, alleviating pain and improving functionality.
Indications: Recommended when conservative treatments are ineffective, and the hip condition significantly impacts daily activities.
Mobility Improvement: The primary goal is to enhance mobility, reduce pain, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with debilitating hip conditions.
Recovery: Post-surgery, a recovery period involves rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and adapt to the new hip joint.
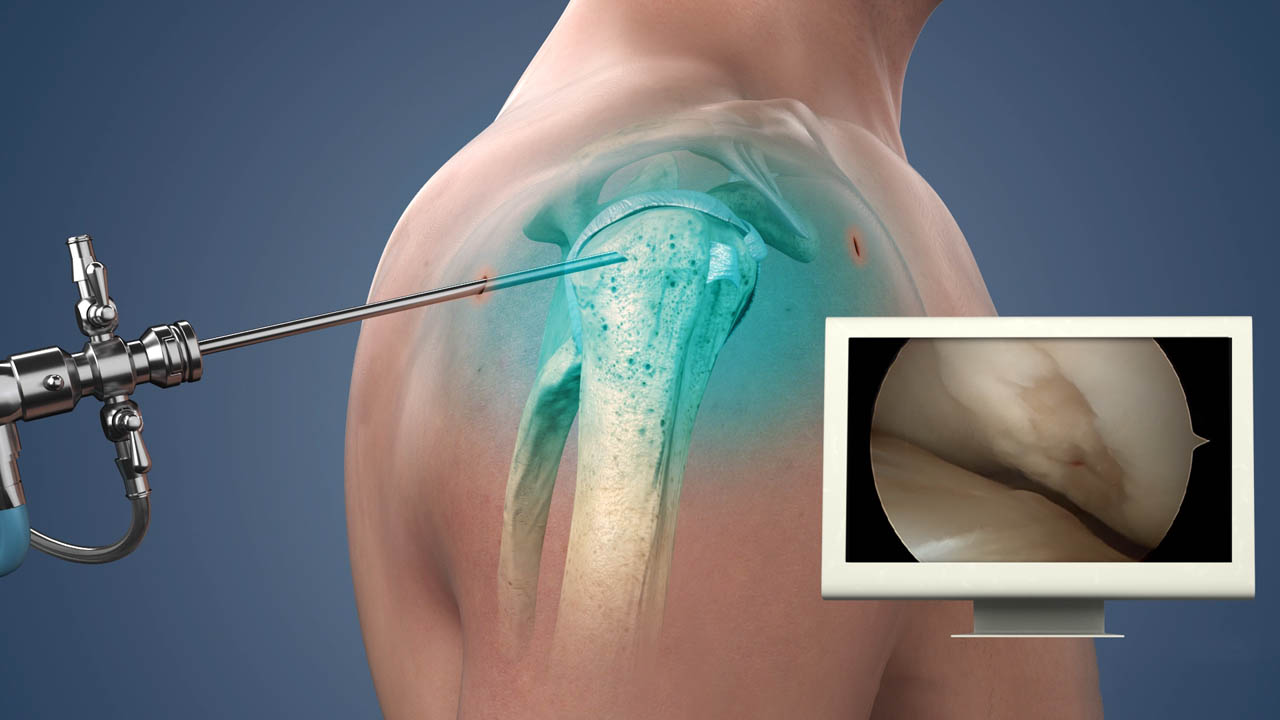
Shoulder Arthroscopy:
Purpose: Shoulder arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure aimed at diagnosing and treating various issues within the shoulder joint.
Procedure: Small incisions are made around the shoulder, and an arthroscope (tiny camera) is inserted to visualize and address problems such as rotator cuff tears or shoulder impingement.
Indications: Commonly used for conditions affecting the shoulder joint, offering advantages like shorter recovery times and less post-operative discomfort compared to traditional open surgery.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic: Besides diagnosis, shoulder arthroscopy allows surgeons to perform therapeutic procedures during the same operation, such as repairing damaged tissues.
Recovery: Typically involves a quicker recovery period and reduced pain, making it a preferred option for certain shoulder conditions. Rehabilitation and physical therapy may be part of the recovery process.

Orthopedic Fracture Repair:
Purpose: Orthopedic fracture repair is a surgical procedure designed to realign and stabilize broken bones, facilitating proper healing.
Procedure: The surgeon uses surgical techniques, such as plates, screws, or other devices, to secure and support the fractured bones, ensuring they heal in the correct alignment.
Indications: Essential for severe fractures that cannot heal adequately on their own or with non-surgical treatments.
Mobility Improvement: The primary goal is to restore the normal alignment of the fractured bones, allowing for proper healing and regaining functionality.
Recovery: Post-surgery, a recovery period involves immobilization, rehabilitation, and physical therapy to promote healing, restore strength, and enhance mobility.
