Joint Replacement & Arthroscopic (Pin-Hole Surgeries)
Joint replacement and arthroscopic surgeries, particularly known for their minimally invasive nature, have transformed the landscape of orthopedic interventions. These procedures, often performed through small incisions, aim to alleviate pain, restore joint function, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals facing joint-related issues.
1. Introduction to Joint Replacement:
Ensure an ergonomic workstation by adjusting chair and desk height, promoting proper alignment, and minimizing strain on the neck and back.Joint replacement involves the removal of damaged joint surfaces, replaced with artificial implants, providing effective solutions for conditions like severe arthritis or joint degeneration.
2. Types of Joint Replacement Surgeries:
Explore various joint replacement surgeries, such as total hip replacement (THR), total knee replacement (TKR), and shoulder replacement. The focus is on precision and customization to address specific joint concerns.
3. Indications for Joint Replacement:
Understand the indications for joint replacement, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and traumatic joint injuries. Rigorous patient assessment and symptom evaluation guide the decision-making process.
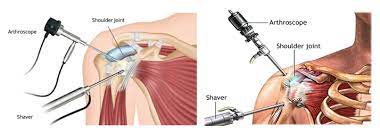
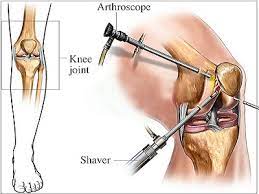
4. Arthroscopic Surgery Overview:
Arthroscopic surgeries, often referred to as pin-hole surgeries, involve the use of a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments to diagnose and treat joint problems through minimally invasive techniques. This is particularly common for knee, shoulder, and ankle issues.
5. Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy:
Explore a range of orthopedic conditions addressed through arthroscopic procedures, such as torn ligaments, meniscus tears, cartilage damage, and joint inflammation. The pin-hole approach allows for targeted and precise treatment.
6. Advantages of Minimally Invasive Techniques:
Highlight the benefits of arthroscopic (pin-hole) surgeries, including smaller incisions, reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and decreased postoperative pain. These advantages contribute to improved patient satisfaction and quicker return to daily activities.
