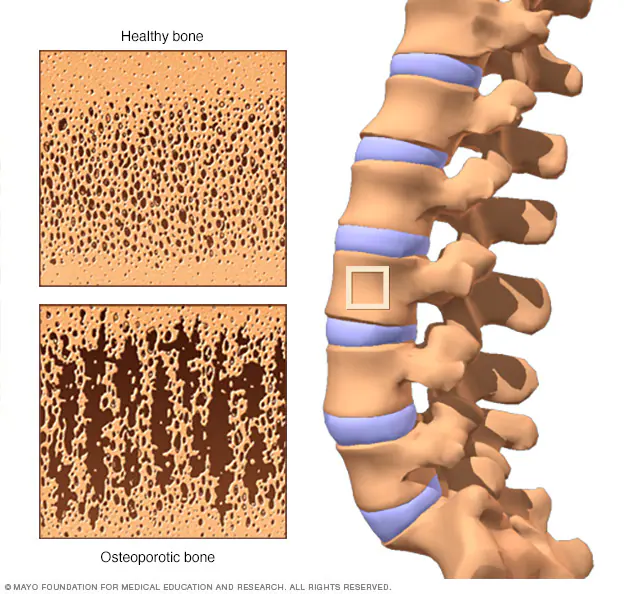
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a bone-thinning disorder that affects both men and women and can lead to fractures. The condition causes bones to become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. Osteoporosis is a condition caused by low bone density and structural changes in the bones. With this condition, there is a decrease in bone density and a change in the structure of the bone matrix — that is, the architecture of collagen fibers
As a result, bones become less dense and more brittle. Without proper treatment, osteoporosis can lead to an increased risk of wrist, hip, and spine fractures. People with osteoporosis are also more likely to suffer from other conditions such as arthritis, low back pain, and chronic pain.
Risk factors for osteoporosis include :
- Age: The risk of osteoporosis increases with age.
- Gender: Women, especially after menopause, are more likely to develop osteoporosis.
- Family history: A family history of osteoporosis increases the risk.
- Body weight: Low body weight or small body frame can be a risk factor.
- Hormone levels: Low estrogen levels in women and low testosterone levels in men are associated with osteoporosis.
- Dietary factors: Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D can contribute to bone loss.
- Physical activity: Lack of exercise or long-term immobility can lead to bone loss.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as glucocorticoids and certain anti-seizure medications, can contribute to bone loss.
